Flow cytometry¶
You’ll learn how to manage a growing number of flow cytometry datasets as a single queryable collection.
Specifically, you will
read a single
.fcsfile as anAnnDataand seed a versioned collection with it (, current page)
append a new dataset (a new
.fcsfile) to create a new version of the collection ()
Setup¶
!lamin init --storage ./test-facs --schema bionty
Show code cell output
💡 connected lamindb: testuser1/test-facs
import lamindb as ln
import bionty as bt
import readfcs
bt.settings.organism = "human" # globally set organism to human
💡 connected lamindb: testuser1/test-facs
ln.settings.transform.stem_uid = "OWuTtS4SApon"
ln.settings.transform.version = "0"
ln.track()
💡 notebook imports: bionty==0.43.1 lamindb==0.72.1 pytometry==0.1.4 readfcs==1.1.8 scanpy==1.10.1
💡 saved: Transform(uid='OWuTtS4SApon6K79', version='0', name='Flow cytometry', key='facs', type='notebook', created_by_id=1, updated_at='2024-05-29 09:59:37 UTC')
💡 saved: Run(uid='iroiApjaQu2JKuCDJJ5W', transform_id=1, created_by_id=1)
Run(uid='iroiApjaQu2JKuCDJJ5W', started_at='2024-05-29 09:59:37 UTC', is_consecutive=True, transform_id=1, created_by_id=1)
Ingest a first artifact¶
Access  ¶
¶
We start with a flow cytometry file from Alpert et al., Nat. Med. (2019).
Calling the following function downloads the artifact and pre-populates a few relevant registries:
ln.core.datasets.file_fcs_alpert19(populate_registries=True)
PosixPath('Alpert19.fcs')
We use readfcs to read the raw fcs file into memory and create an AnnData object:
adata = readfcs.read("Alpert19.fcs")
adata
AnnData object with n_obs × n_vars = 166537 × 40
var: 'n', 'channel', 'marker', '$PnB', '$PnE', '$PnR'
uns: 'meta'
It has the following features:
adata.var.head(10)
| n | channel | marker | $PnB | $PnE | $PnR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1 | Time | 32 | 0,0 | 2097152 | |
| Cell_length | 2 | Cell_length | 32 | 0,0 | 128 | |
| CD57 | 3 | (In113)Dd | CD57 | 32 | 0,0 | 8192 |
| Dead | 4 | (In115)Dd | Dead | 32 | 0,0 | 4096 |
| (Ba138)Dd | 5 | (Ba138)Dd | 32 | 0,0 | 4096 | |
| Bead | 6 | (Ce140)Dd | Bead | 32 | 0,0 | 16384 |
| CD19 | 7 | (Nd142)Dd | CD19 | 32 | 0,0 | 4096 |
| CD4 | 8 | (Nd143)Dd | CD4 | 32 | 0,0 | 4096 |
| CD8 | 9 | (Nd144)Dd | CD8 | 32 | 0,0 | 4096 |
| IgD | 10 | (Nd146)Dd | IgD | 32 | 0,0 | 8192 |
Transform: normalize  ¶
¶
In this use case, we’d like to ingest & store curated data, and hence, we split signal and normalize using the pytometry package.
import pytometry as pm
First, we’ll split the signal from heigh and area metadata:
pm.pp.split_signal(adata, var_key="channel", data_type="cytof")
'area' is not in adata.var['signal_type']. Return all.
adata
AnnData object with n_obs × n_vars = 166537 × 40
var: 'n', 'channel', 'marker', '$PnB', '$PnE', '$PnR', 'signal_type'
uns: 'meta'
Normalize the collection:
pm.tl.normalize_arcsinh(adata, cofactor=150)
Note
If the collection was a flow collection, you’ll also have to compensate the data, if possible. The metadata should contain a compensation matrix, which could then be run by the pytometry compensation function. In the case here, its a cyTOF collection, which doesn’t (really) require compensation.
Validate: cell markers  ¶
¶
First, we validate features in .var using CellMarker:
validated = bt.CellMarker.validate(adata.var.index)
❗ 13 terms (32.50%) are not validated for name: Time, Cell_length, Dead, (Ba138)Dd, Bead, CD19, CD4, IgD, CD11b, CD14, CCR6, CCR7, PD-1
We see that many features aren’t validated because they’re not standardized.
Hence, let’s standardize feature names & validate again:
adata.var.index = bt.CellMarker.standardize(adata.var.index)
validated = bt.CellMarker.validate(adata.var.index)
❗ 5 terms (12.50%) are not validated for name: Time, Cell_length, Dead, (Ba138)Dd, Bead
The remaining non-validated features don’t appear to be cell markers but rather metadata features.
Let’s move them into adata.obs:
adata.obs = adata[:, ~validated].to_df()
adata = adata[:, validated].copy()
Now we have a clean panel of 35 validated cell markers:
validated = bt.CellMarker.validate(adata.var.index)
assert all(validated) # all markers are validated
Register: metadata  ¶
¶
Next, let’s register the metadata features we moved to .obs.
For this, we create one feature record for each column in the .obs dataframe:
features = ln.Feature.from_df(adata.obs)
ln.save(features)
We use the Experimental Factor Ontology through Bionty to create a “FACS” label:
bt.ExperimentalFactor.public().search("FACS").head(2) # search the public ontology
| ontology_id | definition | synonyms | parents | molecule | instrument | measurement | __ratio__ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | ||||||||
| fluorescence-activated cell sorting | EFO:0009108 | A Flow Cytometry Assay That Provides A Method ... | FAC sorting|FACS | [] | None | None | None | 100.0 |
| A/J | EFO:0001327 | A/J Is A Mouse Strain As Described In Jackson ... | AJ|A | [] | None | None | None | 90.0 |
We found one for “FACS”, let’s save it to our in-house registry:
# import the FACS record from the public ontology and save it to the registry
facs = bt.ExperimentalFactor.from_public(ontology_id="EFO:0009108")
facs.save()
We don’t find one for “CyToF”, however, so, let’s create it without importing from a public ontology but label it as a child of “is_cytometry_assay”:
cytof = bt.ExperimentalFactor(name="CyTOF")
cytof.save()
is_cytometry_assay = bt.ExperimentalFactor(name="is_cytometry_assay")
is_cytometry_assay.save()
cytof.parents.add(is_cytometry_assay)
facs.parents.add(is_cytometry_assay)
is_cytometry_assay.view_parents(with_children=True)
❗ record with similar name exists! did you mean to load it?
| uid | name | ontology_id | abbr | synonyms | description | molecule | instrument | measurement | public_source_id | run_id | created_by_id | updated_at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 36GhLFoE | fluorescence-activated cell sorting | EFO:0009108 | None | FAC sorting|FACS | A Flow Cytometry Assay That Provides A Method ... | None | None | None | 51 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:44.606697+00:00 |
Let us look at the content of the registry:
bt.ExperimentalFactor.df()
| uid | name | ontology_id | abbr | synonyms | description | molecule | instrument | measurement | public_source_id | run_id | created_by_id | updated_at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | |||||||||||||
| 3 | 21Qymj4Q | is_cytometry_assay | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | NaN | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:44.644272+00:00 |
| 2 | ogoPdeOk | CyTOF | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | NaN | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:44.638580+00:00 |
| 1 | 36GhLFoE | fluorescence-activated cell sorting | EFO:0009108 | None | FAC sorting|FACS | A Flow Cytometry Assay That Provides A Method ... | None | None | None | 51.0 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:44.606697+00:00 |
Register: data & annotate with metadata  ¶
¶
features = ln.Feature.lookup()
experimental_factors = bt.ExperimentalFactor.lookup()
organisms = bt.Organism.lookup()
artifact = ln.Artifact.from_anndata(
adata, description="Alpert19"
)
artifact.save()
Artifact(uid='ADTN0edI5CUaoHxLHW4v', description='Alpert19', suffix='.h5ad', accessor='AnnData', size=33374864, hash='QNP1c3p6scaAwPo9AW8fLw', hash_type='md5', visibility=1, key_is_virtual=True, created_by_id=1, storage_id=1, transform_id=1, run_id=1, updated_at='2024-05-29 09:59:44 UTC')
artifact.features._add_set_from_anndata(var_field=bt.CellMarker.name)
Inspect the registered artifact¶
Inspect features on a high level:
artifact.features
Feature sets
'var' = 'CD57', 'Cd19', 'Cd4', 'CD8', 'Igd', 'CD85j', 'CD11c', 'CD16', 'CD3', 'CD38', 'CD27', 'CD11B', 'Cd14', 'Ccr6', 'CD94', 'CD86', 'CXCR5', 'CXCR3', 'Ccr7', 'CD45RA'
'obs' = 'Time', 'Cell_length', 'Dead', '(Ba138)Dd', 'Bead'
Inspect low-level features in .var:
artifact.features["var"].df().head()
| uid | name | synonyms | gene_symbol | ncbi_gene_id | uniprotkb_id | organism_id | public_source_id | run_id | created_by_id | updated_at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | |||||||||||
| 1 | 1dPH2YeJqtGd | CD57 | B3GAT1 | 27087 | Q9P2W7 | 1 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:40.380047+00:00 | |
| 2 | 7KaN0QtWWLnk | Cd19 | CD19 | 930 | P15391 | 1 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:40.380164+00:00 | |
| 3 | rKHBZ9JlBdU5 | Cd4 | CD4 | 920 | B4DT49 | 1 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:40.380273+00:00 | |
| 4 | 5YxpB5QNiCWr | CD8 | CD8A | 925 | P01732 | 1 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:40.380378+00:00 | |
| 5 | 7basFKNKrv4j | Igd | None | None | None | 1 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2024-05-29 09:59:40.380489+00:00 |
Use auto-complete for marker names in the var featureset:
markers = artifact.features["var"].lookup()
markers.cd14
CellMarker(uid='5JHfKNo5DC8y', name='Cd14', synonyms='', gene_symbol='CD14', ncbi_gene_id='4695', uniprotkb_id='O43678', created_by_id=1, run_id=1, organism_id=1, public_source_id=26, updated_at='2024-05-29 09:59:40 UTC')
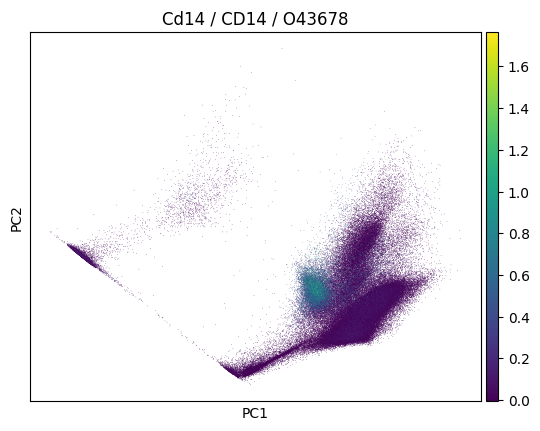
In a plot, we can now easily also show gene symbol and Uniprot ID:
import scanpy as sc
sc.pp.pca(adata)
sc.pl.pca(
adata,
color=markers.cd14.name,
title=(
f"{markers.cd14.name} / {markers.cd14.gene_symbol} /"
f" {markers.cd14.uniprotkb_id}"
),
)
Create a collection from the artifact¶
collection = ln.Collection(
artifact, name="My versioned cytometry collection", version="1"
)
collection
Collection(uid='UlXZqmelGczUxOuo37wz', version='1', name='My versioned cytometry collection', hash='_SSVHoSL17yyiRlHc8Hr', visibility=1, created_by_id=1, transform_id=1, run_id=1)
Let’s inspect the features measured in this collection which were inherited from the artifact:
collection.features
Feature sets
'var' = 'CD57', 'Cd19', 'Cd4', 'CD8', 'Igd', 'CD85j', 'CD11c', 'CD16', 'CD3', 'CD38', 'CD27', 'CD11B', 'Cd14', 'Ccr6', 'CD94', 'CD86', 'CXCR5', 'CXCR3', 'Ccr7', 'CD45RA'
'obs' = 'Time', 'Cell_length', 'Dead', '(Ba138)Dd', 'Bead'
This looks all good, hence, let’s save it:
collection.save()